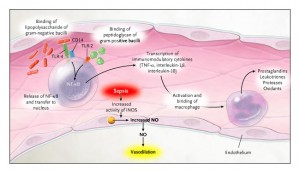
The nursing diagnosis for sepsis is considered to be carried out to find out the infection which is related to invasion of microorganism into the body of patient suffering from sepsis. Sepsis is considered to be a syndrome which is characterized by the clinical symptoms and signs of severe infection which could progress to septic shock or septicemia. The term septicemia would imply to the presence of a specific type of infection which is caused by the repeatedly multiplying growth of microorganism present in blood. It could also be their toxins can may outcome with some of the systemic sepsis and profound psychological changes.
sepsis
The patients with highest risk from the septic shock and bacteremia would include infants, elderly and people who are immune-suppressed with chronic diseases. The long term goals of nursing diagnosis for sepsis are the maintenance of negative cultures by following the antibiotic therapy. The temperature must be maintained below 100 degree of Fahrenheit, the heart rate has to be in between 60 to 100 beats per minutes and the MAP should be higher than 70 mmHq.
DEFINITION SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF SEVERE SEPTIC SHOCK
Sepsis is the body’s response to infection. The body triggers a series of events causing an inflammatory syndrome more or less generalized responsible for hemodynamic and micro circulatory.
There are 3 kinds of sepsis: the 3 phases of successive worsening of the infection and the inflammatory response:
- Sepsis:
- Presence of infection clinically and / or micro-biologically documented
- SIRS = systemic inflammatory response syndrome (presence of at least two of these signs):
- fever> 38.3 ° or <36. ° C
- tachycardia> 90 beats / min
- tachypnea with EN> 20/mn or PaCO2 <32mHg
- Hyper leukocytosis with WBC> 12,000 or <4000/mm3ou> 10% immature forms.
- severe sepsis:
- Onset sepsis and organ dysfunction and / or hypotension corrected by volume and / or lactate> 4 mmol / l
- Septic shock:
- Hypotension secondary to sepsis not only corrected by volume expansion.
Early detection of severe sepsis in reception area
Early recognition of severe sepsis is crucial because earliness of hemodynamic management determines the prognosis.
Immediately detectable signs in reception area and orientation:
- hyperthermia with or without chills.
- chills without fever.
- oliguria.
- decreased level of consciousness, confusion.
- tachypnea> 30.
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- mottled extremities, joints.
- cold extremities and cyanic.
- increased pulse rate> 90 beats / min.
- Systolic BP <90mmHg or <40mmHg compared to normal.
The medical diagnosis of severe sepsis (severe sepsis or septic shock):
Based on the finding of the existence of sepsis associated with hypotension and / or a hyperlactemia> 4 mmol / l and / or organ dysfunction
The diagnostic criteria are:
- SIRS + infection “clinically or microbiologically documented”
- bacteremia (presence of viable organisms in the blood with positive blood cultures)
- pulmonary infection, abdominal, urinary …
At the biological level, sepsis can lead to:
- leukocytosis
- thrombocytopenia (<150 000/mm3)
- Elevation of serum procalcitonin
Organ dysfunction can result in:
- signs of hypoperfusion and / or hypotension.
- an increase of blood lactate (> 4 mmol / l).
- renal failure with creatinine increase (> 20mg / l or more than 50% of the base figure), increased urea and oliguria.
- hepatic failure with increased ALT, AST, GGT, bilirubin> 30mmol / l.
- hypoxia.
- metabolic acidosis results of blood gas.
- signs of DIC.
- encephalopathy or delirium with a Glasgow <14.
The assessment of nursing diagnosis for sepsis
- The temperature of patient would be less than 100 degree Fahrenheit. The cultures would remain negative. The infections are considered to have not spread to patients present in the same unit.
- If there are any positive cultures then it would be recognized within 24 to 48 hours after the nursing diagnosis for sepsis. In other words, there would be positive cultures soon after the offending organism has been identified.
- The patients would not have any symptoms or signs of line infection; which is also termed as Afebrile.
- The patients would start to have negative cultures soon after the treatment has been initiated. It would be after the pertinent antimicrobial treatment.
The rationale of this nursing diagnosis
- There would be decrease with the risk of nosocomial infection or any type of transmission of infection.
- The prime goal is to identify and locate the main source of the infection in patient
- The noscomial infection rate would decrease in time
- The antibiotics of broad spectrum are considered to be intended for the usage against a whole list of organisms. But it is found to be most prudent to make use of narrow spectrum antibiotics to the treatment soon the organism of specific type has been recognized.
The intervention of sepsis nursing diagnosis:
- The hands must be washed before and after every patient care activity. Even in case if usage of gloves.
- The visitors have be isolated and monitored as per the indication.
- Obtain blood, wound, sputum, urine and cultures soon after the initial suspicion of the onset of sepsis.
- The aseptic techniques have to be followed very strictly. Even at the time of handling some of the equipments and invasive lines.
- The broad spectrum of antibiotics has to be initiated and it has to be changed to narrow spectrum soon as the culture results have been gathered.
Final Results:
After about 8 hours of nursing interventions the patient would start recovering and will heal in timely manner. The final end results of nursing diagnosis for sepsis is considered to be that, patient suffering from sepsis would be free from any type of further infection. It would be as per the evidence found from negative cultures. The glucose level present in the blood stream would be less than 150 mg or dL.