Pathology:
COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
COPD should be reported immediately, so that nursing diagnosis for COPD could be performed. This is because the issue is serious and can put your life at stake. COPD is a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. As the name shows, this is obstructive illness of lungs which stays for longer time. If it is not treated immediately, it can damage the respiratory system seriously causing a threat against the life of the patient. Smoking is largely responsible for causing this inflammation. Tobacco and other chemicals present in smoke of cigarette are highly damaging to respiratory organs and decreases the normal life span of a smoker. If COPD is confirmed in any patient, during nursing diagnosis for COPD, smoking should be immediately abandoned. Only this way, the life expectancy of the patient can be increased.
Causes of COPD:
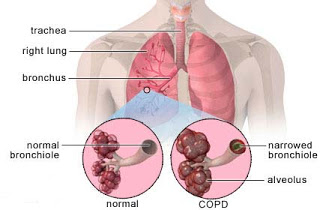
Chronic obstructive disease can be either due to chronic bronchitis or due to emphysema. In some cases, both are reported at the same time. In both cases, the respiratory track gets blocked, and short breathing happens.
Chronic bronchitis affects the goblet cells of the respiratory tract. These calls are responsible for production of mucus, a thick secretion, which plays an important role in entrapping germs. In chronic bronchitis, these cells swell and increase in size. Resultantly, the large amount of sputum is produced, which blocks the respiratory track and leads to difficult breathing. Coughing is also produced with or without mucus. This factor is kept in focus during nursing diagnosis for COPD.
Emphysema affects the alveoli of the lung and decreases their surface area. The septum present in the alveoli for increasing surface area is damaged, and volume of alveoli is increased. This increase in volume decreases the surface area available for gaseous exchange and patient face difficulty in breathing. Crackling and wheezing in the chest also occurs in emphysema. These sounds play an important role in nursing diagnosis of COPD.
Smoking aggravates chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cause inflammation of lungs and its epithelial membrane.
Air pollution is also reported as a frequent cause of COPD.
Occupation also matters. People working in coal mines or polluted conditions are more prone to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This is an important factor of consideration during nursing diagnosis for COPD.
Bacteria and virus also cause COPD.
Genetic factors are also responsible for various pulmonary diseases.
Signs and symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:
Different signs and symptoms which arise due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are as follows:
1.Wheezing
2.Tachypnea (rapid rate of breathing)3.Excessive mucus production
4.Cough with or without sputum
5.Chest tightness
6.Difficult breathing
7.Cyanosis (blue coloration of lips and skin)
All these symptoms are associated with effort to take a long breathe. In this condition, the patient cannot breathe enough air, and hypoxia can also occur. The oxygen supply lessens, and blood is not oxygenated completely. As a result, other body parts also do not get blood with enough oxygen and blue coloration of skin is observed particularly in areas like lips and tips of fingers. This is called cyanosis, and patients are said to be blue bloaters.
Objectives:
1.Remove bronchial secretions in order to improve pulmonary ventilation and gas exchange.
2.Prevent and reduce pulmonary infection.
3.Improving the nutritional status of the patient.
4.Provide psychosocial support to the patient.
Diagnosis:
1.Hypoxemia related to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
2.Possibility of infection related to disordered lung function.
3.Altered nutrition (less than body requirements) regarding dyspnea to mealtimes, loss of muscle mass, sticky sputum, potassium depletion.
4.Difficulty with emotional problems and instability associated with dyspnea and fatigue.
Activities:
1.Administer medications or inhalers that produce broncho dilation.
2.Listening to the chest after administration of aerosol broncho dilators for evaluating air flow improvement and reduction of adventitious breath sounds.
3.Make micronebulizaciones to humidify the bronchial tree and liquefy the sputum.
4.Use postural drainage to help clear secretions, as the cause purulent airway obstruction.
5.Instruct patient to cough
6.Identify the initial manifestations of respiratory infections: increased design, fatigue, change in color, amount and character of sputum, nervousness, irritability, fever.
7.Get sputum smear and culture.
8.Administer prescribed antibiotics (ampicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline.
9.In patients with prolonged antibiotic newspapers to do sputum cultures for possible superinfection.
10.Advise the patient to avoid coming into contact with people with respiratory tract infections.
110Give as prescribed corticosteroids, these drugs have anti-inflammatory and
12.Consequence help relieve airway obstruction.
13.Recommend six small meals daily if the patient has designs: even a small increase of abdominal contents can press the diaphragm and cause breathlessness.
14.Offer a hyper protein diet with snacks between meals to improve counter caloric intake and weight loss.
15.Avoid foods that cause abdominal discomfort.
16.Give supplemental oxygen when the patient eats, to relieve breathlessness.
17.Understand that the steady shortening of breath and fatigue make the patient is irritable, apprehensive, anxious and depressed with feelings of helplessness and despair.
18.Assess whether the patient’s behavior in reaction (anger, depression, acceptance.)
19.Demonstrate a positive attitude in the patient concerned: listen and show that we care about him. Be sensitive to their fears, anxieties and depression, which helps provide emotional relief and insight.
Results:
1.The patient shows correction of hypoxemia.
2.The patient avoids infection and seek treatment when it occurs.
3.The patient improved nutritional status: synchronized meals to coincide with periods of improvement in breathing, rest before and after meals.
4.The patient has improved emotional attitude, expressing feelings; looking for a support group.
Nursing diagnosis for COPD:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease can be diagnosed by considering various factors. The occurrence of these factors may vary from patient to patient. Some of them are common among all the individuals and always come in observation during nursing diagnosis for COPD. These include:
1.Large airway resistance
2.Bronchoconstriction3.Anorexia (nutrition less than requirements of the body)
4.Rhonchi, i.e. crackling sounds heard in stethoscope.
5.Pulmonary infection and airway blockage
6.Anxiety and stress
7.Dyspnea, i.e. shortness of breath.
During nursing diagnosis for COPD all or some of these factors are observed.